-
 Ultra-processed foods: Leading cause of 'chronic disease pandemic,' scientists warnUltra-processed foods (UPFs) are a leading cause of the "chronic disease pandemic" linked to diet, with food firms putting profit above all else, global experts have warned.... Read more
Ultra-processed foods: Leading cause of 'chronic disease pandemic,' scientists warnUltra-processed foods (UPFs) are a leading cause of the "chronic disease pandemic" linked to diet, with food firms putting profit above all else, global experts have warned.... Read more -
 Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to EuropePreviously unknown volcanic eruptions may have kicked off an unlikely series of events that brought the Black Death—the most devastating pandemic in human history—to the shores of medieval Europe, new research has revealed.... Read more
Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to EuropePreviously unknown volcanic eruptions may have kicked off an unlikely series of events that brought the Black Death—the most devastating pandemic in human history—to the shores of medieval Europe, new research has revealed.... Read more -
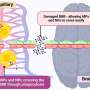 Five ways microplastics may harm your brainMicroplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain.... Read more
Five ways microplastics may harm your brainMicroplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain.... Read more -
 Rising temperatures linked to shorter, poorer sleep for US adultsHigher nighttime temperatures are linked to shorter sleep times and lower sleep quality, especially for people with chronic health conditions, lower socioeconomic status, or those living on the West Coast, according to a new USC study. Researchers estimate that by 2099, people could lose up to 24 hours of sleep... Read more
Rising temperatures linked to shorter, poorer sleep for US adultsHigher nighttime temperatures are linked to shorter sleep times and lower sleep quality, especially for people with chronic health conditions, lower socioeconomic status, or those living on the West Coast, according to a new USC study. Researchers estimate that by 2099, people could lose up to 24 hours of sleep... Read more -
 Beyond biology: Why social context is the key for improving modern medicineA new series in The Lancet led by a UC Berkeley professor equips policymakers and clinicians with a toolkit to break out of silos and make more informed health decisions.... Read more
Beyond biology: Why social context is the key for improving modern medicineA new series in The Lancet led by a UC Berkeley professor equips policymakers and clinicians with a toolkit to break out of silos and make more informed health decisions.... Read more -
 Worried after sunscreen recalls? Here's how to choose a safe oneMost of us know sunscreen is a key way to protect areas of our skin not easily covered by clothes from excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation.... Read more
Worried after sunscreen recalls? Here's how to choose a safe oneMost of us know sunscreen is a key way to protect areas of our skin not easily covered by clothes from excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation.... Read more -
 How to host a meal if one of your guests has an eating disorder or is anxious around foodAs the festive season approaches, perhaps you're thinking of hosting friends and family.... Read more
How to host a meal if one of your guests has an eating disorder or is anxious around foodAs the festive season approaches, perhaps you're thinking of hosting friends and family.... Read more -
 When holiday leftovers linger, reset your eating habits for a new yearA new year offers new beginnings and an opportunity to reset your eating habits after the holidays. Andrea Delgado, a Mayo Clinic dietitian, says it's best to eliminate what you don't need, including party food leftovers.... Read more
When holiday leftovers linger, reset your eating habits for a new yearA new year offers new beginnings and an opportunity to reset your eating habits after the holidays. Andrea Delgado, a Mayo Clinic dietitian, says it's best to eliminate what you don't need, including party food leftovers.... Read more -
 Are mosquito repellents safe to use? And do I really need them in Australia?Summer's here and after a wet spring in many parts of Australia, mosquitoes are out in force. Insect repellent has become a routine requirement for time outdoors.... Read more
Are mosquito repellents safe to use? And do I really need them in Australia?Summer's here and after a wet spring in many parts of Australia, mosquitoes are out in force. Insect repellent has become a routine requirement for time outdoors.... Read more -
 Shredded cheese recalled over possible metal fragments, FDA saysA large recall of shredded cheese sold under several popular grocery store brands is now underway after the manufacturer reported the product may contain small metal fragments, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).... Read more
Shredded cheese recalled over possible metal fragments, FDA saysA large recall of shredded cheese sold under several popular grocery store brands is now underway after the manufacturer reported the product may contain small metal fragments, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).... Read more -
 Internet use may protect caregivers against lonelinessStaying connected through the internet can help older adults who care for their family or friends feel less lonely and cope better with the stress of caregiving, according to a new study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and published in the journal JMIR Aging.... Read more
Internet use may protect caregivers against lonelinessStaying connected through the internet can help older adults who care for their family or friends feel less lonely and cope better with the stress of caregiving, according to a new study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and published in the journal JMIR Aging.... Read more -
 Kennedy's vaccine advisory committee delays vote on hepatitis B shots for newbornsA federal vaccine advisory committee on Thursday voted to delay a decision on whether newborns should still get the hepatitis B vaccine on the day they're born.... Read more
Kennedy's vaccine advisory committee delays vote on hepatitis B shots for newbornsA federal vaccine advisory committee on Thursday voted to delay a decision on whether newborns should still get the hepatitis B vaccine on the day they're born.... Read more -
 Managing food allergies and dietary restrictions during the holidaysA plate of freshly baked cookies, a glass of perfectly garnished eggnog. For many, these images may conjure up warm memories and the anticipation of the forthcoming holiday season.... Read more
Managing food allergies and dietary restrictions during the holidaysA plate of freshly baked cookies, a glass of perfectly garnished eggnog. For many, these images may conjure up warm memories and the anticipation of the forthcoming holiday season.... Read more -
 Harmful exposure to metal discovered in recycling center employeesThe metal recycling industry is growing, not least due to the use of metals in green energy electronic components. Researchers at Lund University have examined the inhaled air of workers at 13 recycling companies in Sweden. Among the results, high levels of lead in air and elevated levels of multiple... Read more
Harmful exposure to metal discovered in recycling center employeesThe metal recycling industry is growing, not least due to the use of metals in green energy electronic components. Researchers at Lund University have examined the inhaled air of workers at 13 recycling companies in Sweden. Among the results, high levels of lead in air and elevated levels of multiple... Read more -
 The do's and don'ts of cold weather sports: A physical therapist offers adviceWinter sports are extreme by nature: Freezing temperatures, slick surfaces, whiteout conditions, and sharp blades can all make injury more likely.... Read more
The do's and don'ts of cold weather sports: A physical therapist offers adviceWinter sports are extreme by nature: Freezing temperatures, slick surfaces, whiteout conditions, and sharp blades can all make injury more likely.... Read more
© 2024 E-RADIO.CA - CANADA'S LATEST TECH NEWS HEADLINES, STORIES AND MORE.
