-
 New large language model helps patients understand their radiology reportsImagine getting an MRI of your knees and being told you have "mild intrasubstance degeneration of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus."... Read more
New large language model helps patients understand their radiology reportsImagine getting an MRI of your knees and being told you have "mild intrasubstance degeneration of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus."... Read more -
 AI detects fatty liver disease with chest X-raysFatty liver disease, caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver, is estimated to affect one in four people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, making it crucial to detect early and initiate treatment.... Read more
AI detects fatty liver disease with chest X-raysFatty liver disease, caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver, is estimated to affect one in four people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, making it crucial to detect early and initiate treatment.... Read more -
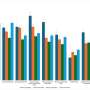 COVID-19 pandemic significantly eroded American public's trust in US public health institutions, assessment showsFour discrete cross-sectional surveys of US adults from 2020–2024 reveal US adults reporting high confidence in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) dropped from 82% in February 2020 to a low of 56% in June 2022, according to a study published in PLOS Global Public Health by Amyn... Read more
COVID-19 pandemic significantly eroded American public's trust in US public health institutions, assessment showsFour discrete cross-sectional surveys of US adults from 2020–2024 reveal US adults reporting high confidence in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) dropped from 82% in February 2020 to a low of 56% in June 2022, according to a study published in PLOS Global Public Health by Amyn... Read more -
 Got an emotional wellness app? It may be doing more harm than goodSophisticated new emotional wellness apps powered by AI are growing in popularity.... Read more
Got an emotional wellness app? It may be doing more harm than goodSophisticated new emotional wellness apps powered by AI are growing in popularity.... Read more -
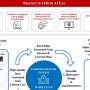 Using data and AI to create better health care systemsAcademic medical centers could transform patient care by adopting principles from learning health systems principles, according to researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine and the University of California, San Diego. In this approach, information from electronic health records, clinical trials and day-to-day hospital operations is analyzed in real-time to uncover insights... Read more
Using data and AI to create better health care systemsAcademic medical centers could transform patient care by adopting principles from learning health systems principles, according to researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine and the University of California, San Diego. In this approach, information from electronic health records, clinical trials and day-to-day hospital operations is analyzed in real-time to uncover insights... Read more -
 AI in health care needs patient-centered regulation to avoid discrimination, say expertsA new commentary published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine warns that current risk-based regulatory approaches to artificial intelligence (AI) in health care fall short in protecting patients, potentially leading to over- and undertreatment as well as discrimination against patient groups.... Read more
AI in health care needs patient-centered regulation to avoid discrimination, say expertsA new commentary published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine warns that current risk-based regulatory approaches to artificial intelligence (AI) in health care fall short in protecting patients, potentially leading to over- and undertreatment as well as discrimination against patient groups.... Read more -
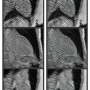 AI-assisted model enhances low-quality MRI heart scansAn AI-assisted model developed by researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine and the School of Engineering can take low-quality MRI heart scans and turn them into high-quality images, while reducing the time needed to scan the heart by about 90%.... Read more
AI-assisted model enhances low-quality MRI heart scansAn AI-assisted model developed by researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine and the School of Engineering can take low-quality MRI heart scans and turn them into high-quality images, while reducing the time needed to scan the heart by about 90%.... Read more -
 How AI is becoming a new social presence that could change human relationships and brain functionsAs artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots and virtual agents become part of everyday life—from customer service and health care to personal companionship—a critical question arises: How do these AI interactions affect social and emotional dynamics?... Read more
How AI is becoming a new social presence that could change human relationships and brain functionsAs artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots and virtual agents become part of everyday life—from customer service and health care to personal companionship—a critical question arises: How do these AI interactions affect social and emotional dynamics?... Read more -
 AI tool can interpret echocardiograms in minutesCardiologists use echocardiography to diagnose a range of functional or structural abnormalities of the heart. Using more than 100 videos and images that capture different parts of the heart, echocardiographers make dozens of measurements, such as the heart's size and shape, ventricle thickness, and the movement and function of each... Read more
AI tool can interpret echocardiograms in minutesCardiologists use echocardiography to diagnose a range of functional or structural abnormalities of the heart. Using more than 100 videos and images that capture different parts of the heart, echocardiographers make dozens of measurements, such as the heart's size and shape, ventricle thickness, and the movement and function of each... Read more -
 Sleep data from wearable device may help predict preterm birthPreterm birth complications are the primary cause of death among children under age 5, and nearly 75% could be prevented with interventions, according to the World Health Organization. While the causes leading to preterm birth are largely unknown, an interdisciplinary research team at Washington University in St. Louis has found... Read more
Sleep data from wearable device may help predict preterm birthPreterm birth complications are the primary cause of death among children under age 5, and nearly 75% could be prevented with interventions, according to the World Health Organization. While the causes leading to preterm birth are largely unknown, an interdisciplinary research team at Washington University in St. Louis has found... Read more -
 Strengths, gaps and opportunities of AI in health professions educationStudents in health-related fields are benefiting from generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) in many areas of learning, but concerns about critical thinking and reduced peer interaction have come to light in a new systematic review conducted by Monash University.... Read more
Strengths, gaps and opportunities of AI in health professions educationStudents in health-related fields are benefiting from generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) in many areas of learning, but concerns about critical thinking and reduced peer interaction have come to light in a new systematic review conducted by Monash University.... Read more -
 Guidance issued for GPs managing weight-loss injection patientsAcademics at King's College London and the University of East Anglia have released guidance for GPs on how to manage patients who may be privately accessing weight loss drugs.... Read more
Guidance issued for GPs managing weight-loss injection patientsAcademics at King's College London and the University of East Anglia have released guidance for GPs on how to manage patients who may be privately accessing weight loss drugs.... Read more -
 Smart sensors and smarter health: How AI and wearables are reimagining preventive health careWhen it comes to automobiles, no matter how well they are maintained, at some point the check engine light is going to come on. Inevitably, a look under the hood or trip to the mechanic is in order. The human body doesn't have a check engine light, but wearable sensors... Read more
Smart sensors and smarter health: How AI and wearables are reimagining preventive health careWhen it comes to automobiles, no matter how well they are maintained, at some point the check engine light is going to come on. Inevitably, a look under the hood or trip to the mechanic is in order. The human body doesn't have a check engine light, but wearable sensors... Read more -
 AI helps to detect dangerous colon polypsColorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in Europe, but timely screening can be highly effective in preventing it. Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for this purpose. It enables potentially dangerous colon polyps to be detected and removed at an early stage. However, accurately distinguishing... Read more
AI helps to detect dangerous colon polypsColorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in Europe, but timely screening can be highly effective in preventing it. Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for this purpose. It enables potentially dangerous colon polyps to be detected and removed at an early stage. However, accurately distinguishing... Read more -
 Predicting cognitive abilities from brain scansPredicting cognitive abilities from brain imaging has long been a central goal in cognitive neuroscience. While machine learning has modestly improved predictions using brain MRI data, most studies rely on a single MRI modality.... Read more
Predicting cognitive abilities from brain scansPredicting cognitive abilities from brain imaging has long been a central goal in cognitive neuroscience. While machine learning has modestly improved predictions using brain MRI data, most studies rely on a single MRI modality.... Read more
© 2024 E-RADIO.CA - CANADA'S LATEST TECH NEWS HEADLINES, STORIES AND MORE.
