-
 Genetic testing reveals often-overlooked fungal infections in California clinicsA new study reveals that a rarely-diagnosed and frequently drug-resistant species, Aspergillus tubingensis, may be one of the most common causes of fungal infections in Southern California.... Read more
Genetic testing reveals often-overlooked fungal infections in California clinicsA new study reveals that a rarely-diagnosed and frequently drug-resistant species, Aspergillus tubingensis, may be one of the most common causes of fungal infections in Southern California.... Read more -
 Key kidney sensor that helps control fluid balance identifiedA new study has identified a critical "pressure sensor" inside the kidney that helps the body control blood pressure and fluid levels. The finding helps explain how the kidneys sense changes in blood volume—something scientists for decades have known occurs but didn't have a mechanistic explanation.... Read more
Key kidney sensor that helps control fluid balance identifiedA new study has identified a critical "pressure sensor" inside the kidney that helps the body control blood pressure and fluid levels. The finding helps explain how the kidneys sense changes in blood volume—something scientists for decades have known occurs but didn't have a mechanistic explanation.... Read more -
 From lab to clinic: Phase I trial of promising combination therapy for resistant ovarian cancerResearchers at the University of Colorado Cancer Center have discovered a novel therapy combination that could offer new hope to ovarian cancer patients who do not respond to existing treatments. Conducted entirely at the University of Colorado Anschutz, this research has advanced from the laboratory to a Phase I clinical... Read more
From lab to clinic: Phase I trial of promising combination therapy for resistant ovarian cancerResearchers at the University of Colorado Cancer Center have discovered a novel therapy combination that could offer new hope to ovarian cancer patients who do not respond to existing treatments. Conducted entirely at the University of Colorado Anschutz, this research has advanced from the laboratory to a Phase I clinical... Read more -
 Poor kidney health linked to higher levels of Alzheimer's biomarkers in bloodPeople with impaired kidney function have higher levels of Alzheimer's biomarkers in their blood, but not an increased risk of dementia, according to a study published in Neurology.... Read more
Poor kidney health linked to higher levels of Alzheimer's biomarkers in bloodPeople with impaired kidney function have higher levels of Alzheimer's biomarkers in their blood, but not an increased risk of dementia, according to a study published in Neurology.... Read more -
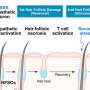 Why stress can make your hair fall out: A two-part reactionIt's well known that stress can trigger hair loss. A new paper explores how this happens and how our response to stress can have long-term consequences for our scalps, research that may eventually yield insights into autoimmune diseases.... Read more
Why stress can make your hair fall out: A two-part reactionIt's well known that stress can trigger hair loss. A new paper explores how this happens and how our response to stress can have long-term consequences for our scalps, research that may eventually yield insights into autoimmune diseases.... Read more -
 Intervention aims to enhance self-determination of young people with intellectual disabilityBetween 0.7% and 1.5% of people in developed countries are estimated to suffer from intellectual disability (ID). In Spain, this is equivalent to more than 400,000 people. The term intellectual disability refers to a set of significant limitations in intellectual functioning and learning that manifest before the individual's 18th birthday... Read more
Intervention aims to enhance self-determination of young people with intellectual disabilityBetween 0.7% and 1.5% of people in developed countries are estimated to suffer from intellectual disability (ID). In Spain, this is equivalent to more than 400,000 people. The term intellectual disability refers to a set of significant limitations in intellectual functioning and learning that manifest before the individual's 18th birthday... Read more -
 Antibody designed to guide immune cells against hard-to-treat cancer typesA cancer-targeting antibody that helps the body's immune cells spot and destroy hard-to-treat tumors such as triple-negative breast cancer has been developed by researchers.... Read more
Antibody designed to guide immune cells against hard-to-treat cancer typesA cancer-targeting antibody that helps the body's immune cells spot and destroy hard-to-treat tumors such as triple-negative breast cancer has been developed by researchers.... Read more -
 Internet and lack of trust threatens patient–doctor bondPhysicians have worked to earn the trust of their patients for nearly 2,400 years, dating back to the days of Hippocrates, the father of Western medicine. Lucky for Hippocrates that his patients didn't have internet access.... Read more
Internet and lack of trust threatens patient–doctor bondPhysicians have worked to earn the trust of their patients for nearly 2,400 years, dating back to the days of Hippocrates, the father of Western medicine. Lucky for Hippocrates that his patients didn't have internet access.... Read more -
 Largest study of nose microbiome helps highlight those at risk of Staph aureus infectionPeople who persistently carry Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in their nose have fewer species of other bacteria, while certain bacteria may help to prevent S. aureus colonization. These are the findings of the largest-ever study of the nasal microbiome, published in Nature Communications.... Read more
Largest study of nose microbiome helps highlight those at risk of Staph aureus infectionPeople who persistently carry Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in their nose have fewer species of other bacteria, while certain bacteria may help to prevent S. aureus colonization. These are the findings of the largest-ever study of the nasal microbiome, published in Nature Communications.... Read more -
 Stem cell organoids mimic aspects of early limb developmentScientists at EPFL have created a scalable 3D organoid model that captures key features of early limb development, revealing how a specialized signaling center shapes both cell identity and tissue organization.... Read more
Stem cell organoids mimic aspects of early limb developmentScientists at EPFL have created a scalable 3D organoid model that captures key features of early limb development, revealing how a specialized signaling center shapes both cell identity and tissue organization.... Read more -
 Singing mice speak volumes: Brain mechanisms behind song production explored in new researchAll mice squeak, but only some sing. Scotinomys teguina, aka Alston's singing mice, hail from the cloud forests of Costa Rica. More than 2,000 miles north, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) neuroscientists study these musically gifted mammals to better understand the evolutionary origins of vocal communication. Their research could also... Read more
Singing mice speak volumes: Brain mechanisms behind song production explored in new researchAll mice squeak, but only some sing. Scotinomys teguina, aka Alston's singing mice, hail from the cloud forests of Costa Rica. More than 2,000 miles north, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) neuroscientists study these musically gifted mammals to better understand the evolutionary origins of vocal communication. Their research could also... Read more -
 Patients are more than participants: What meaningful engagement really looks like—and why it improves health researchWhen we talk about "patient engagement" in research, it can sound like a slogan on a grant application rather than something that changes people's lives.... Read more
Patients are more than participants: What meaningful engagement really looks like—and why it improves health researchWhen we talk about "patient engagement" in research, it can sound like a slogan on a grant application rather than something that changes people's lives.... Read more -
 The 'Miracle Mineral Solution'—amazing cure or toxic illusion?Miracle Mineral Solution, also known as MMS, has been marketed for years as a purported miracle cure for various conditions, including cancer, autism, and COVID-19. MMS is the marketing name for sodium chlorite (NaClO₂), a powerful disinfectant used, among other things, for water treatment. When sodium chlorite is acidified, chlorine... Read more
The 'Miracle Mineral Solution'—amazing cure or toxic illusion?Miracle Mineral Solution, also known as MMS, has been marketed for years as a purported miracle cure for various conditions, including cancer, autism, and COVID-19. MMS is the marketing name for sodium chlorite (NaClO₂), a powerful disinfectant used, among other things, for water treatment. When sodium chlorite is acidified, chlorine... Read more -
 Bird flu viruses are resistant to fever, making them a major threat to humansBird flu viruses are a particular threat to humans because they can replicate at temperatures higher than a typical fever, one of the body's ways of stopping viruses in their tracks, according to new research led by the universities of Cambridge and Glasgow.... Read more
Bird flu viruses are resistant to fever, making them a major threat to humansBird flu viruses are a particular threat to humans because they can replicate at temperatures higher than a typical fever, one of the body's ways of stopping viruses in their tracks, according to new research led by the universities of Cambridge and Glasgow.... Read more -
 When ribosomes collide, cells launch emergency stress defensesRibosomes, the protein factories of the cell, are essential for all living organisms. They bind to mRNA and move along the messenger molecule, reading the genetic code as they go. Using this information, they link amino acids to make proteins.... Read more
When ribosomes collide, cells launch emergency stress defensesRibosomes, the protein factories of the cell, are essential for all living organisms. They bind to mRNA and move along the messenger molecule, reading the genetic code as they go. Using this information, they link amino acids to make proteins.... Read more
© 2024 E-RADIO.CA - CANADA'S LATEST TECH NEWS HEADLINES, STORIES AND MORE.
